Recent investigations have uncovered a concerning infection chain leveraging fake CAPTCHA pages to distribute malware, particularly Lumma Stealer. This campaign, observed by McAfee Labs and highlighted in findings from CloudSEK, targets users globally, illustrating the extensive reach of this attack method.
Infection Vectors Identified
The infection chain involves two primary vectors leading users to fake CAPTCHA pages:
1. Cracked Game Download URLs: Users seeking pirated games are redirected to malicious CAPTCHA pages.
2. Phishing Emails: Users, especially those associated with GitHub, receive emails urging them to address a fictitious "security vulnerability" in a repository, directing them to harmful URLs.
The ClickFix Mechanism
The ClickFix infection chain deceives users into clicking buttons like “Verify you are a human.” Once clicked, a malicious script is copied to the clipboard, and users are then misled into pasting the script after pressing the Windows key + R, unknowingly executing the malware. This method simplifies the infection process, enabling attackers to deploy malware seamlessly.
Detailed Attack Vectors
1. Cracked Gaming Software Download URLs
When users search for free or cracked versions of popular games, they often encounter links on online forums that redirect them to fake CAPTCHA pages.
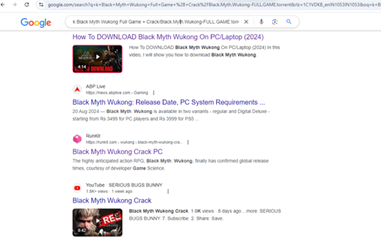
For instance, a public Runkit notebook may host a malicious link, which leads to these harmful sites when accessed. After clicking the CAPTCHA button, a malicious PowerShell script is copied to the clipboard, prompting users to execute it.
.png?width=602&height=301&name=6718fd257b615863a76e3e2a_6718fae4dc0835d7bce87f0b_Emerging%20Threat%20The%20ClickFix%20Infection%20Chain%20and%20Lumma%20Stealer%20Malware%20(3).png)
The website utilises JavaScript to facilitate this action, employing Base64 encoding to obscure the script’s content. Upon decoding, it is revealed that the script uses the mshta utility to execute embedded malicious scripts while ignoring the binary component of the file. This tactic allows the malware to go undetected, as it operates from common directories like the Temp folder.
2. Phishing Emails Impersonating GitHub
The second vector targets GitHub contributors with phishing emails claiming a “security vulnerability.” When users click the links, they are redirected to fake CAPTCHA pages where malicious scripts are executed in a similar manner. This script retrieves PowerShell commands that download Lumma Stealer samples from external servers, facilitating further compromise.
Lumma Stealer: The Malware Behind the Attack
Lumma Stealer has emerged as a potent threat, specifically designed to harvest sensitive information from infected systems. Upon installation, it can extract credentials, personal data, and financial information, which can then be exploited by cybercriminals. The effectiveness of Lumma Stealer is heightened by its distribution method through fake CAPTCHA pages, making it easier for attackers to gain access to user systems.
Detection and Mitigation Strategies
To combat this infection chain and the associated Lumma Stealer malware, organisations should adopt a multi-faceted approach:
• URL Blocking: Prevent access to known fake CAPTCHA pages.
• Heuristic Blocking: Detect and block malicious uses of the mshta utility.
• User Education: Conduct regular training sessions to inform users about social engineering tactics and phishing schemes.
• Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software: Ensure up-to-date software is installed on all endpoints.
• Email Filtering: Implement robust filters to block phishing emails and malicious attachments.
• Network Segmentation: Limit the spread of malware within the organisation by segmenting the network.
• Patch Management: Keep all operating systems, software, and applications updated with the latest security patches.
• Avoiding Untrusted Downloads: Educate users to avoid downloading cracked software or visiting suspicious websites.
• Verifying URLs: Encourage users to verify URLs in emails, especially from unknown or unexpected sources.
• Monitoring: Regularly check the Temp folder for unusual or suspicious files.
Conclusion and Recommendations
The ClickFix infection chain and Lumma Stealer malware highlight how cybercriminals exploit common user behaviours, such as downloading cracked software or responding to phishing emails, to distribute malicious payloads. By leveraging fake CAPTCHA pages, attackers successfully deceive users into executing scripts that lead to malware installation.
To protect against these sophisticated threats, organisations should implement the recommended mitigations and maintain a proactive stance against evolving cyber risks.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
Here are some IoCs associated with this threat:
Fake CAPTCHA Websites
• Ofsetvideofre[.]click/
• Newvideozones[.]click/veri[.]html
• Clickthistogo[.]com/go/67fe87ca-a2d4-48ae-9352-c5453156df67?var_3=F60A0050-6F56-11EF-AA98-FFC33B7D3D59
Malware Samples
• SHA256:
o b6a016ef240d94f86e20339c0093a8fa377767094276730acd96d878e0e1d624 (PowerShell)
o d737637ee5f121d11a6f3295bf0d51b06218812b5ec04fe9ea484921e905a207 (Executable)
By remaining vigilant and implementing these strategies, organisations can enhance their defences against the ClickFix infection chain and the threat of Lumma Stealer malware.